低氘氫水實驗室 研究項目
- 極超高純氫氣研究—7N、8N維米製程氫氣
- 固態儲氫器研究、太空船用固態儲氫器研究
- 低氘飽和氫水製程研究及應用研究
- 低氘水用於生物實驗及製藥應用研究
- 氫氣呼吸之劑量及物理效應研究
- 低氘水用於育苗育種農業生技研究
- 氫氣用於食品科學研究
- 低氘水用於食品科學研究
- 呼吸氫氣及低氘飽和氫水之於癌症、中風、巴金森症、妥瑞症、糖尿病、心肌損傷、肝損傷、腦中風、放射治療損傷、老年癡呆、心肌硬塞、痛風、COPD、異位性皮膚炎、僵直性脊椎炎、過敏、紅斑性狼瘡及自體免疫性疾病之觀察研究
氫氣對牙周炎誘導的動脈硬化具有治療作用
已有 1169 次閱讀 2012-5-22 13:36 |個人分類:飲用氫氣水|系統分類:科研筆記|關鍵字:牙周炎 氫氣 office www.h2-water.com
動脈粥樣硬化是以大血管泡沫細胞脂肪沉積為特徵的進展性疾病。氧化的低密度脂蛋白在動脈粥樣硬化發生發展中發揮重要作用,而氧化的低密度脂蛋白是由於氧化應激引起,隨後導致內皮細胞啟動和炎症反應,並導致炎症細胞浸潤,巨噬細胞吞噬低密度脂蛋白,變成泡沫細胞。儘管對具體機制不清楚,但研究表明許多引起氧化應激的危險因素如吸煙、糖尿病、高血脂、高血壓和牙周病等都是引起動脈硬化的重要因素。牙周病是一種常見炎症性疾病,損傷周圍可以產生過量活性氧,許多研究認為牙周病和心血管疾病關係密切,和動脈硬化的發生存在相關關係。有研究發現,牙周病可導致系統活性氧和氧化低密度脂蛋白增加,根據這個發現,使用抗氧化治療可作為干預牙周病引起的動脈粥樣氧化的手段。
氫氣分子的選擇性抗氧化作用發現後,作為一種新型的抗氧化物質,通過飲用氫氣水對動脈硬化具有治療作用已經被證明。那麼氫氣水可否具有阻斷牙周病誘導的動脈硬化值得探討。
這個研究假定氫氣可以降低血液中氧化低密度脂蛋白,阻斷牙周病誘導的動脈氧化應激,從對動脈硬化具有治療作用。
本研究使用乙醯賴氨酸(hexanoyl-lysine (HEL))作為早期氧化指標、硝基酪氨酸(蛋白硝基化)和8-OHdG(核酸氧化指標)作為評價動脈氧化應激的指標。血清活性氧代謝產物reactive oxygen metabolites (ROM)作為循環系統氧化應激的指標。
局部組織動脈硬化相關指標,牙齒周圍病理改變,動脈硬化形態學觀察。研究結果發現,氫氣水對牙周病及其誘導的動脈硬化均有顯著改善效果。提示氫氣水可能可作為該類疾病的治療手段。
台灣氫水實驗室 TEL:0963-210-763
email: ddh2water@gmail.com LINE ID:h2water
台灣氫水實驗室部落格:http://blog.xuite.net/hworker77086600/twblog
歡迎來電索取氫水辨認方法(防止喝到傷身的假氫水)
氫水,氫分子、氫氣、健康氫水,水素水,負電位,ORP,抗氧化,抗自由基,氫分子醫學,氫水,Hydrogen water,氫氣、氫,台灣氫水研究中心,氫思語,孫學軍,太田成男,鹼性離子水,小分子水,能量水,電解水,富氫水,負氫水,活水,健康,養生,活力,大氫鬆,小氫鬆,氫水機,水素,水素水機,王群光,氫氧機,綠加利,活美水素水,低氘水,活性原子氫,富氫水,負氫水,每日水素,活氫水,氫氧造水機,百樂,負氫,氫博士,氫水棒,氫源,新德美,HOH,鹼性活氫水,氫美機,負氫離子水,氫氣棒,呼吸氫氣,氫氧療法,加氫水,氫水、健康氫水、水素水、負電位、ORP、抗氧化、抗自由基 、氫分子醫學、氫水、Hydrogen water、氫氣、氫、氫水、台灣氫水實驗室、台灣氫水研究中心、氫思語、孫學軍、太田成男、鹼性離子水、小分子水、能量水、電解水、富氫水、負氫水、活水、健康、養生、活力、大氫鬆、小氫鬆、氫水機、水素、水素水機、王群光、氫氧機、綠加利、活美水素水、低氘水、活性原子氫、富氫水、負氫水、每日水素、活氫水、氫氧造水機、百樂、負氫、氫博士、氫水棒、氫源、新德美、HOH、鹼性活氫水、氫美機、負氫離子
提供玻璃瓶裝飽和氫水供對比,免費兩瓶給你測試,收運費120元。(運費是宅配業者收去的)
Hydrogen-rich water prevents lipid deposition in the.pdf
Hydrogen-rich water prevents lipid deposition in the descending aorta in a rat periodontitis model
• Daisuke Ekunia, • Takaaki Tomofujia, , ,
• a Department of Preventive Dentistry, Okayama University Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2-5-1 Shikata-cho, Kita-ku, Okayama 700-8558, Japan
• http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2012.04.013, How to Cite or Link Using DOI
Objective
Periodontitis has been causally linked to atherosclerosis, which is mediated by the oxidative stress. As hydrogen-rich water (HW) scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS), we hypothesized that HW could prevent lipid deposition induced by periodontitis in the aorta. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of HW on the initiation of atherosclerosis in a rat periodontitis model.
Design
Eighteen 8-wk-old male Wistar rats were divided into three groups of six rats; the periodontitis group, periodontitis + HW group and the no treatment (control) group. In the periodontitis and periodontitis + HW groups, periodontitis was induced using a ligature for 4 wk, while the periodontitis + HW group was given water containing 800–1000 μg/L hydrogen during the 4-wk experimental period.
Results
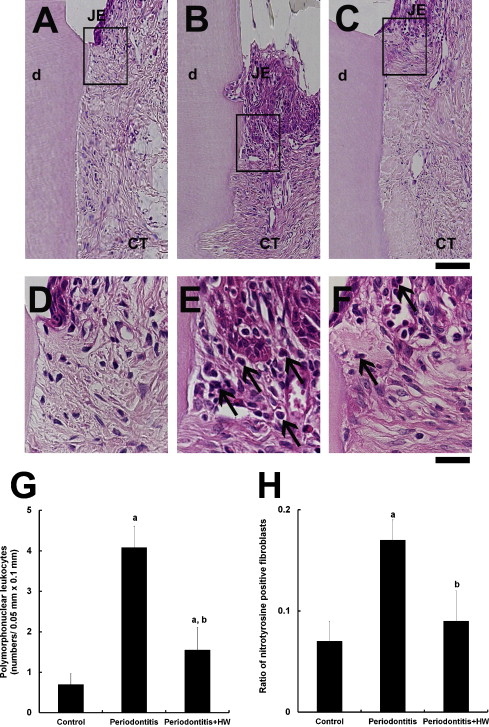
In the periodontitis group, lipid deposition in the descending aorta was observed. The periodontitis group also showed significant higher serum levels for ROS and oxidised low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (ox-LDL) (1.7 and 1.4 times, respectively), and higher aortic expression levels of nitrotyrosine and hexanoyl-lysine (HEL) (7.9 and 16.0 times, respectively), as compared to the control group (p < 0.05). In the periodontitis + HW group, lipid deposition was lower. Lower serum levels of ROS and ox-LDL (0.46 and 0.82 times, respectively) and lower aortic levels of nitrotyrosine and HEL (0.27 and 0.19 times, respectively) were observed in the periodontitis + HW group than in the periodontitis group (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
HW intake may prevent lipid deposition in the rat aorta induced by periodontitis by decreasing serum ox-LDL levels and aortic oxidative stress.
Abbreviations

